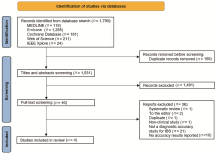
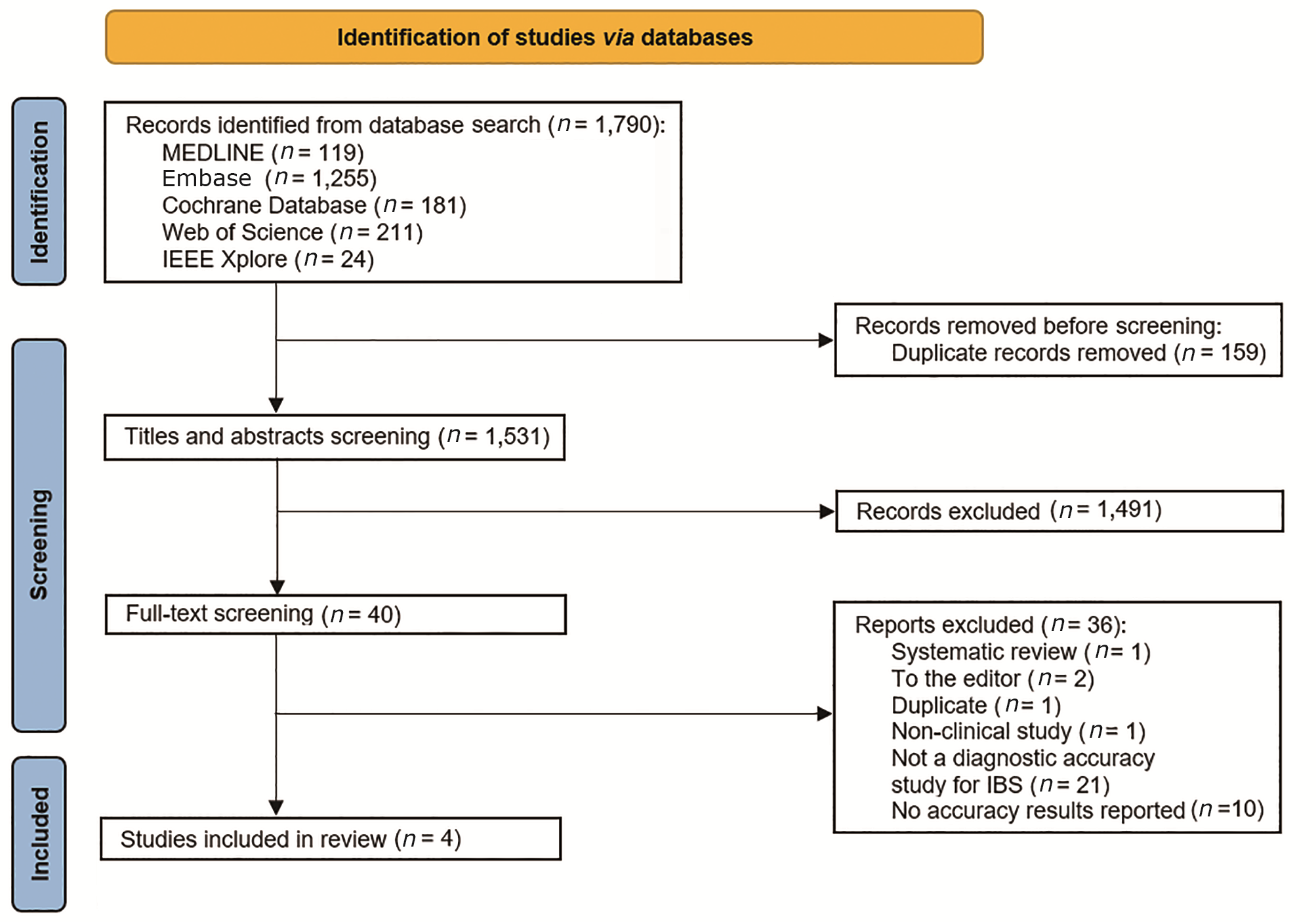
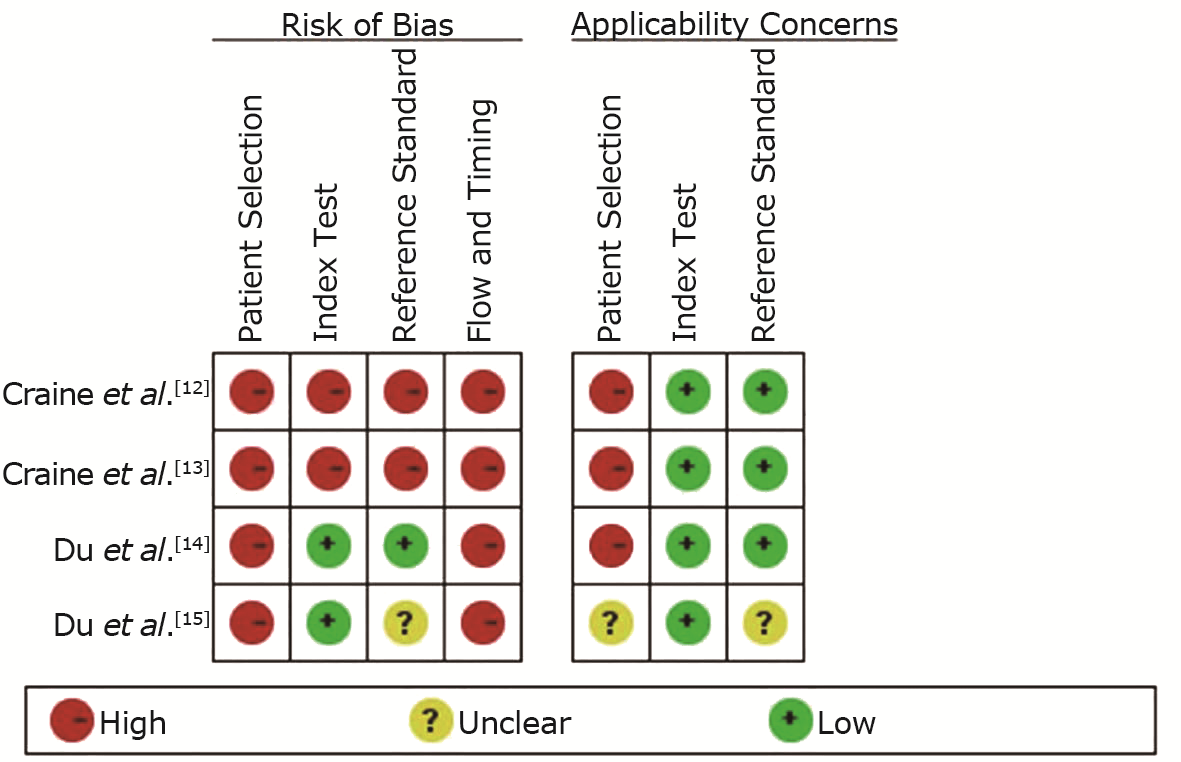
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 122-130.doi: 10.24920/004307
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Diagnostic Accuracy of Computerized Bowel Sound Analysis with Non-Invasive Devices for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Xia-Xiao Yan1, 2#, Yue-Lun Zhang3#, Yu-Pei Zhang2#, Ying-Yun Yang1, Dong Wu1, *( )
)
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, State Key Laboratory of Complex Severe and Rare Diseases, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2Eight-Year Medical Doctor Program, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
3Medical Research Center, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
-
Received:2023-10-16Accepted:2024-02-07Published:2024-06-30Online:2024-04-10 -
Contact:*wudong@pumch.cn -
About author:#co-first author:Contributed equally to the article.
Cite this article
Xia-Xiao Yan, Yue-Lun Zhang, Yu-Pei Zhang, Ying-Yun Yang, Dong Wu. Diagnostic Accuracy of Computerized Bowel Sound Analysis with Non-Invasive Devices for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2024, 39(2): 122-130.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1.
Demographical and clinical characteristics of the included studies"
| Study | Country | Study design | Clinical setting | Recruitment | Subject no. | Mean age (yrs) | Male: female: transgender | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Controls | Patients | Controls | ||||||
| Craine et al. [ | USA | Case- control | Gastroenterology Clinic at the Alameda County Medical Center | From medical center | Volunteers from a community | 18 | 15 | NA | 11:22:0 |
| Craine et al.[ | USA | Case-control | Gastroenterology Clinic at the Alameda County Medical Center | From medical center | Volunteers from a community and patients presenting with conditions unrelated to abdominal discomfort | 45 | 37 | 43.6 | 31:51:0 |
| Du et al.[ | Australia | Case-control | Marshall Center, the University of Western Australia | Advertisment and media interviews | Advertisment and media interviews | 15 | 15 | 34.2 | 5:24:1 |
| Du et al.[ | NA | Case-control | NA | NA | NA | 33 | 32 | NA | NA |
Table 2.
Overview of bowel sound analysis and reference standard in the included studies"
| Studies | Reference standard | Bowel sound analysis | Diagnostic performance of bowel sound analysis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recording | Analysis | Index | TP (n) | FP (n) | FN (n) | TN (n) | Se | Sp | |||
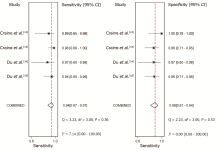
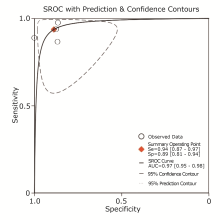
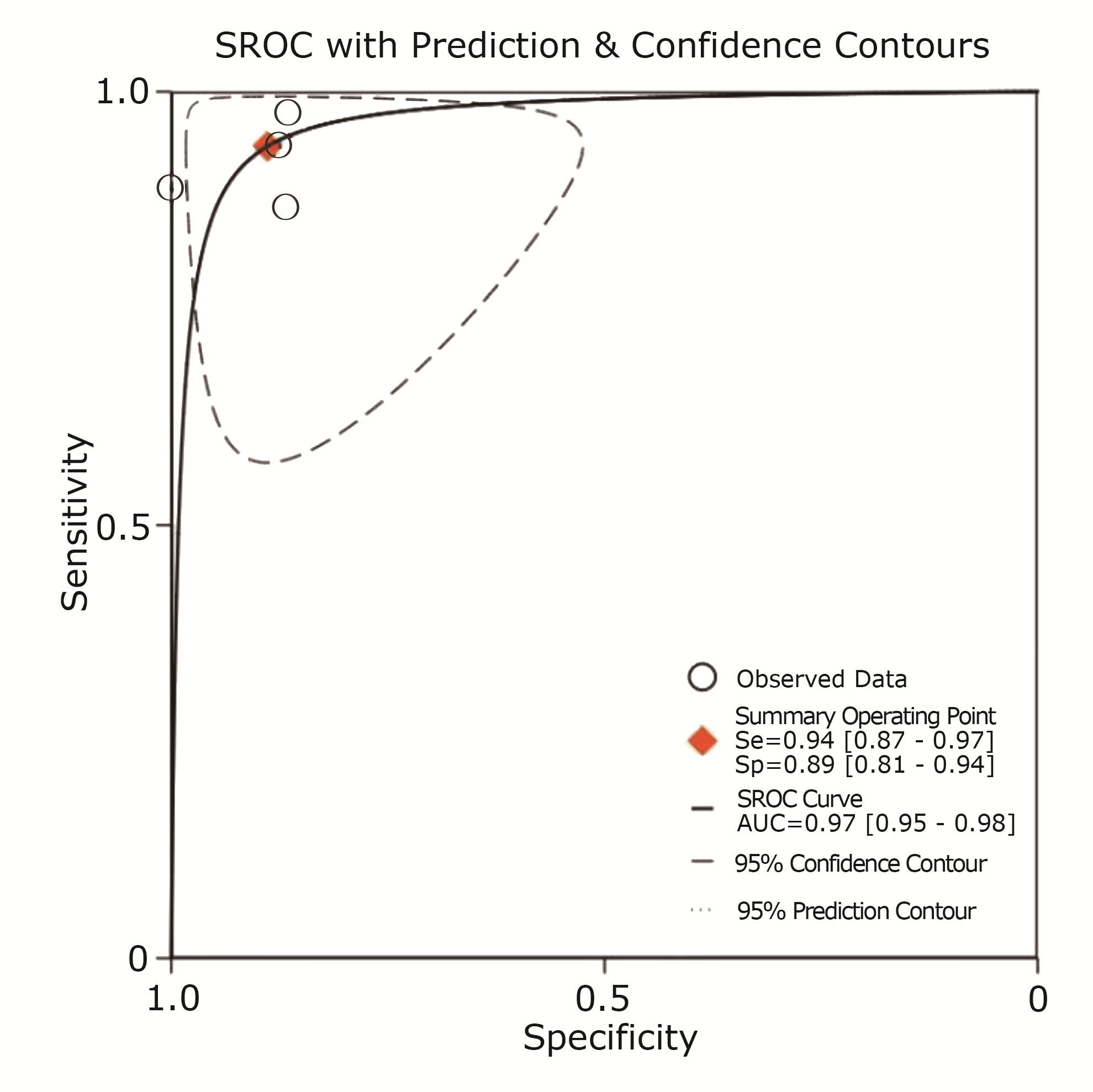
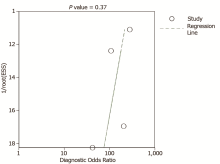
| Craine et al.[ | Rome criteria. Persistent or recurring symptoms for at least one year | Electronic stethoscope on right lower quadrant of the abdomen | Creative WaveStudio software package | Sound-to-sound interval > 640 ms | 16 | 0 | 2 | 15 | 0.89 | 1.00 | |
| Craine et al.[ | Rome criteria. At least two clinic visits to verify the IBS diagnosis | Electronic stethoscope on the right side of the umbilicus | Enterotach software | Sound-to-sound interval > 740 ms | 44 | 5 | 1 | 32 | 0.98 | 0.86 | |
| Du et al.[ | A formal diagnosis of IBS, symptoms persisting for at least six months, no organic cause for the symptoms after a colonoscopy within the past ten years (typically within the past five years) | Zoom H6 handy recorder connected to four piezoelectric transducers on four quadrants of the abdomen | Logistic regression machine learning model and testing | Acoustic index of IBS calculated from 26 bowel sounds features | 13 | 2 | 2 | 13 | 0.87 | 0.87 | |
| Du et al.[ | Not reported. An existing clinical diagnosis of IBS | Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems microphones on four quadrants of the abdomen | Logistic regression machine learning model and testing | A model based on 13 acoustic features related to motility and shifting motion complex and two symptom features | 31 | 4 | 2 | 28 | 0.94 | 0.88 | |
| 1. |
Drossman DA, Hasler WL. Rome IV-functional GI disorders: disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology 2016; 150(6):1257-61. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.035.
pmid: 27147121 |
| 2. | Lovell RM, Ford AC. Global prevalence of and risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10(7):712-21.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.02.029. |
| 3. |
Black CJ, Ford AC. Global burden of irritable bowel syndrome: trends, predictions and risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; 17(8):473-86. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-0286-8.
pmid: 32296140 |
| 4. | Mearin F, Lacy BE, Chang L, et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2016; 150(6):1393-407.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031. |
| 5. |
Spiegel BM, Farid M, Esrailian E, et al. Is irritable bowel syndrome a diagnosis of exclusion?: a survey of primary care providers, gastroenterologists, and IBS experts. Am J Gastroenterol 2010; 105(4): 848-58. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.47.
pmid: 20197761 |
| 6. | Ford AC, Lacy BE, Talley NJ. Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med 2017; 376(26):2566-78. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1607547. |
| 7. | Palsson OS, Whitehead WE, van Tilburg MA, et al. Development and validation of the Rome IV diagnostic questionnaire for adults. Gastroenterology 2016; 150(6):1481-91. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.014. |
| 8. |
O'Connor OJ, McSweeney SE, McWilliams S, et al. Role of radiologic imaging in irritable bowel syndrome: evidence-based review. Radiology 2012; 262(2):485-94. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11110423.
pmid: 22156992 |
| 9. | Sood R, Gracie DJ, Law GR, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the accuracy of diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome with symptoms, biomarkers and/or psychological markers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015; 42(5):491-503. doi: 10.1111/apt.13283. |
| 10. | Vulpoi RA, Luca M, Ciobanu A, et al. The potential use of artificial intelligence in irritable bowel syndrome management. Diagnostics (Basel) 2023; 13(21):3336. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213336. |
| 11. |
Zaborski D, Halczak M, Grzesiak W, et al. Recording and analysis of bowel sounds. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol 2015; 5(2):67-73. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1137.
pmid: 29201695 |
| 12. | Craine BL, Silpa M, O'Toole CJ. Computerized auscultation applied to irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 1999; 44(9):1887-92. doi: 10.1023/a:1018859110022. |
| 13. | Craine BL, Silpa ML, O'Toole CJ. Enterotachogram analysis to distinguish irritable bowel syndrome from Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci 2001; 46(9):1974-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1010651602095. |
| 14. | Du X, Allwood G, Webberley KM, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome via bowel sound features: proof of concept. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2019; 10(3):e00017. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000017. |
| 15. | Du X, Webberley KM, Marshall BJ. Highly seneitive diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome via non-invasive methods. Gastroenterology 2020; 158(6):S855. |
| 16. | Wang F, Wu D, Jin P, et al. A flexible skin-mounted wireless acoustic device for bowel sounds monitoring and evaluation. Science China (Information Sciences) 2019; 62(10):171-81. |
| 17. | Salameh JP, Bossuyt PM, McGrath TA, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies (PRISMA-DTA): explanation, elaboration, and checklist. BMJ 2020; 370:m2632. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2632. |
| 18. |
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 2011; 155(8):529-36. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.
pmid: 22007046 |
| 19. |
Emoto T, Shono K, Abeyratne UR, et al. ARMA-based spectral bandwidth for evaluation of bowel motility by the analysis of bowel sounds. Physiol Meas 2013; 34(8):925-36. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/34/8/925.
pmid: 23893043 |
| 20. | Dimoulas C, Kalliris G, Papanikolaou G, et al. Bowel-sound pattern analysis using wavelets and neural networks with application to long-term, unsupervised, gastrointestinal motility monitoring. Expert Systems Applications 2008; 34(1):26-41. |
| 21. | Dimoulas CA. Audiovisual spatial-audio analysis by means of sound localization and imaging: a multimedia healthcare framework in abdominal sound mapping. IEEE Trans Multimedia 2016; 18(10):1969-76. |
| 22. | Huang Y, Song I, Rana P, et al. Fast diagnosis of bowel activities. 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks; 2017 May 14-19; Anchorage, AK, USA. New York: IEEE; 2017. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2017.7966234. |
| 23. | Zhao K, Jiang H, Wang Z, et al. Long-term bowel sound monitoring and segmentation by wearable devices and convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 2020; 14(5): 985-96. doi: 10.1109/tbcas.2020.3018711. |
| 24. | Inderjeeth AJ, Webberley KM, Muir J, et al. The potential of computerised analysis of bowel sounds for diagnosis of gastrointestinal conditions: a systematic review. Syst Rev 2018; 7(1): 124. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0789-3. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|